PowerShell Basics
Back to ConfigMgr main menu
Back to ConfigMgr & PowerShell menu
Windows PowerShell is Microsoft's task automation and configuration management framework, consisting of a command line shell and associated scripting language built on .NET Framework. It is a valuable administration tool as it combines the speed of a command line with the flexibility of a scripting language.
PowerShell commands are referred to as Cmdlets. All cmdlets are made up of two parts: a verb and a noun. They are separated by a hyphen ‘-‘ character.
Some cmdlets are integrated with Windows, and others are installed with programs like ConfigMgr.
Launch PowerShell by clicking on this icon on the taskbar. (Open PowerShell as Administrator by right clicking - you should do this as most of the cmdlets you will be using will require this)
You can also search by typing PowerShell.
(Note that we need the x86 version - the ConfigMgr Admin Console is a 32-bit application)
Note the PS telling you that you are running PowerShell
Some useful commands
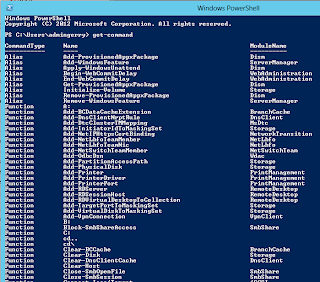
get-command gives you a list of all available PowerShell commands
See the verbs that can be used in cmdlets. Each verb can be used with in conjunction with various nouns to create powerful cmdlets
Add
Block
Clear
Close
Connect
Copy
Disable
Disconnect
Dismount
Enable
End
Export
Format
Get
Grant
Initialize
Import
Install
Invoke
Join
Limit
Measure
Merge
Mount
Move
New
Open
Optimize
Publish
Register
Remove
Rename
Repair
Reset
Resize
Resolve
Restore
Restart
Resume
Revoke
Save
Select
Send
Set
Show
Start
Stop
Suspend
Sync
Test
Unblock
Undo
Uninstall
Unregister
Update
Use
Wait
Write
get-command -verb Get
This will list all the Get cmdlets
Example
Get-service
Try this (use a service that you are allowed to stop - requires PowerShell to be run as administrator)
Get-Service -name WsusService
Stop-Service -name WsusService
Get-Service -name WsusService
Start the service again
Start-Service -name WsusService
Verify that it is started
Get-Service -name WsusService
Back to ConfigMgr & PowerShell menu
Windows PowerShell is Microsoft's task automation and configuration management framework, consisting of a command line shell and associated scripting language built on .NET Framework. It is a valuable administration tool as it combines the speed of a command line with the flexibility of a scripting language.
PowerShell commands are referred to as Cmdlets. All cmdlets are made up of two parts: a verb and a noun. They are separated by a hyphen ‘-‘ character.
Some cmdlets are integrated with Windows, and others are installed with programs like ConfigMgr.
Launch PowerShell by clicking on this icon on the taskbar. (Open PowerShell as Administrator by right clicking - you should do this as most of the cmdlets you will be using will require this)
You can also search by typing PowerShell.
(Note that we need the x86 version - the ConfigMgr Admin Console is a 32-bit application)
Note the PS telling you that you are running PowerShell
Some useful commands
get-command gives you a list of all available PowerShell commands
See the verbs that can be used in cmdlets. Each verb can be used with in conjunction with various nouns to create powerful cmdlets
Add
Block
Clear
Close
Connect
Copy
Disable
Disconnect
Dismount
Enable
End
Export
Format
Get
Grant
Initialize
Import
Install
Invoke
Join
Limit
Measure
Merge
Mount
Move
New
Open
Optimize
Publish
Register
Remove
Rename
Repair
Reset
Resize
Resolve
Restore
Restart
Resume
Revoke
Save
Select
Send
Set
Show
Start
Stop
Suspend
Sync
Test
Unblock
Undo
Uninstall
Unregister
Update
Use
Wait
Write
get-command -verb Get
This will list all the Get cmdlets
Example
Get-service
Try this (use a service that you are allowed to stop - requires PowerShell to be run as administrator)
Get-Service -name WsusService
Stop-Service -name WsusService
Get-Service -name WsusService
Start the service again
Start-Service -name WsusService
Verify that it is started
Get-Service -name WsusService







No comments:
Post a Comment